Google Photos will include a concealed watermark on images that have been edited using AI.
Google’s investment in AI is well-known and becomes apparent as soon as you open any of its software products. The Google Photos app has been among the first to benefit from this focus on AI. Now, the company is offering some transparency regarding its features.
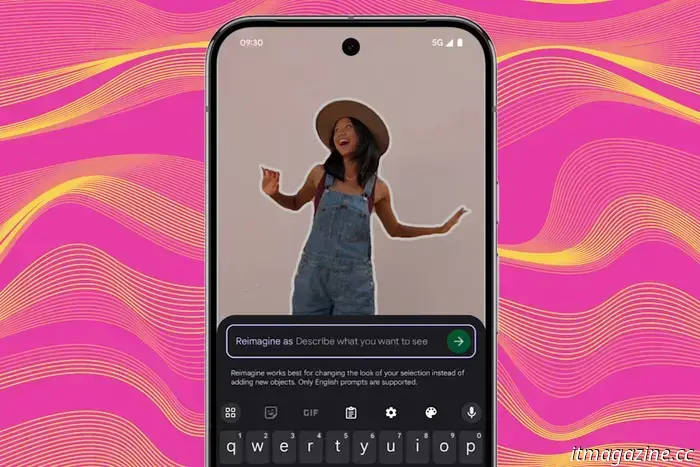
Do you recall the Magic Editor, which allows you to edit photos using AI? From now on, images that have been altered with the Reimagine tool within the Magic Editor will include an invisible watermark.
The Reimagine feature allows users to make edits by using natural language commands. You simply need to choose the elements you'd like to modify and then describe the changes in a sentence. It can alter backgrounds, remove specific objects, and introduce new elements, among other capabilities.
However, this watermark won’t be visible, as it is applied at the Pixel level in photos that have undergone AI editing. Google is utilizing the SynthID digital watermarking tool to tag images that have been artistically enhanced by its AI.
It’s important to note that it may not always provide accurate labeling, particularly with subtle alterations. "In some instances, edits performed with Reimagine might be too minute for SynthID to label and identify — such as changing the color of a small flower in the background of an image," the company stated.
SynthID was created by Google DeepMind as a digital watermarking solution for visual media generated by AI. This watermark is not visible to the human eye, but can be detected by machines and online platforms, including Google Search.
When a watermark is embedded in a photo, it does not compromise the image quality. Even if the AI-edited image is cropped, the color profile altered, filters applied, or compression occurs, SynthID will still preserve the AI signature.
In addition to images produced by Google's Imagen model, SynthID is also integrated into videos created by the Veo video generation model.
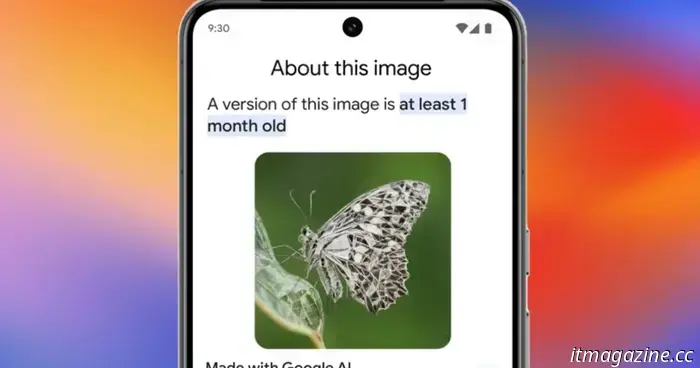
You can verify the role of AI editing in a photo by reviewing the “About this image” section. This information is accessible for online images through the Chrome browser and within Google Image Search.
This section not only provides the date when an image was initially indexed by Google Search and where it first appeared online but also includes details about its AI origins.
The "About this image" information can also be accessed using the Circle to Search feature on smartphones and through Google Lens in the Google mobile app available for both Android and iOS. The extent of copyright protection for such images varies depending on the level of AI involvement.
Google’s method differs from standards like C2PA, which are also gaining popularity and utilize cryptographic techniques to alter image metadata. Notably, Google is a committee member of the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA), which includes other organizations such as Amazon, Meta, OpenAI, and Microsoft.

Other articles
 The Leica LUX Grip aims to enhance your iPhone photography.
Leica Camera AG is among the top camera manufacturers worldwide. Nevertheless, it recognizes that smartphones are the main cameras for millions of users around the planet. This is the context for the newly released accessory for iPhone. The new grip, which costs $329, connects to your iPhone through MagSafe technology, providing your phone with the sensation […]
The Leica LUX Grip aims to enhance your iPhone photography.
Leica Camera AG is among the top camera manufacturers worldwide. Nevertheless, it recognizes that smartphones are the main cameras for millions of users around the planet. This is the context for the newly released accessory for iPhone. The new grip, which costs $329, connects to your iPhone through MagSafe technology, providing your phone with the sensation […]
 I discovered my new favorite fighting game with the help of Capcom Fighting Collection 2.
Capcom Fighting Collection 2 includes many classic titles, but its most thrilling games are the hidden gems from the Dreamcast era.
I discovered my new favorite fighting game with the help of Capcom Fighting Collection 2.
Capcom Fighting Collection 2 includes many classic titles, but its most thrilling games are the hidden gems from the Dreamcast era.
 NYT Mini Crossword today: solutions for Thursday, February 6.
The NYT Mini crossword may be significantly smaller than a standard crossword, but it's still quite challenging. If you're having trouble with today's puzzle, we have the solutions for you.
NYT Mini Crossword today: solutions for Thursday, February 6.
The NYT Mini crossword may be significantly smaller than a standard crossword, but it's still quite challenging. If you're having trouble with today's puzzle, we have the solutions for you.
 Photography enthusiasts will be excited about the design of this forthcoming phone.
The soon-to-be-released Xiaomi 15 Ultra may resemble a well-known camera. Check it out.
Photography enthusiasts will be excited about the design of this forthcoming phone.
The soon-to-be-released Xiaomi 15 Ultra may resemble a well-known camera. Check it out.
 Miles Teller has a single wish for Tom Cruise regarding Top Gun 3.
Will there be a Top Gun 3? If Miles Teller returns to the cockpit, he has a particular request for Tom Cruise.
Miles Teller has a single wish for Tom Cruise regarding Top Gun 3.
Will there be a Top Gun 3? If Miles Teller returns to the cockpit, he has a particular request for Tom Cruise.
 Significant Apple foldables could be coming in the near future.
Apple might utilize an anticipated foldable iPhone as a testing platform for a future foldable iPad or MacBook.
Significant Apple foldables could be coming in the near future.
Apple might utilize an anticipated foldable iPhone as a testing platform for a future foldable iPad or MacBook.
Google Photos will include a concealed watermark on images that have been edited using AI.
Any photos that gain creative advantages from AI through the Magic Editor's Reimagine feature will be watermarked at the pixel level within the Google Photos application.
