Why NVIDIA RTX PCs provide the optimal solution for running AI locally.
NVIDIA’s RTX AI PCs provide data center-level AI capabilities on desktops, empowering enthusiasts, creators, and developers to run sophisticated models locally, at a faster pace, and with improved control.
AI has integrated into daily computing through cloud-based chatbots and online services, and now it’s available directly on personal computers. From creative software and productivity tools to developer applications and research tasks, there is a growing desire among users to operate AI applications on their personal machines according to their own preferences.
As this trend gains momentum, the emphasis is moving from what AI can achieve to the environments in which it functions best. For users concerned with performance, privacy, costs, and flexibility, the significance of the underlying hardware has intensified. AI models are resource-heavy, and efficient execution demands substantial computing power.
NVIDIA’s RTX AI PCs are specifically engineered for such tasks. Equipped with NVIDIA GeForce RTX GPUs, these systems incorporate the foundational technologies seen in top AI data centers, delivering the performance, software compatibility, and efficiency necessary for contemporary AI tasks.
Who is interested in running AI on their PCs today?
As AI becomes more ingrained in everyday tasks, the reliance on always-active cloud services is transitioning towards a preference for swift, private, and manageable AI that runs directly on personal computers.
The audience for local AI is more extensive than many may realize, encompassing three distinct groups, each with unique motivations.
Productivity-oriented users are a significant demographic utilizing AI assistants. These individuals seek tools that can summarize documents, search through local files, and deliver contextual insights based on their personal data. For them, AI serves as an instrument for optimizing daily activities, which often entails keeping their data on local systems.
The second group includes creators. Artists, designers, and video editors are embracing AI technologies. Tools such as diffusion models in ComfyUI, AI-facilitated video editing, and 3D generation streamline repetitive tasks, accelerate the creative process, and introduce new methodologies—all while allowing users to operate within familiar applications.
The third group consists of developers—students, hobbyists, independent engineers, and researchers. As AI capabilities broaden, developers require hardware that allows them to construct, test, refine, and optimize models locally. Relying on cloud-based resources or incurring costs per use can restrict experimentation and stifle innovation.
Despite their differences, all three groups share a common need for dependable local performance without reliance on cloud services.
Why opt for local AI instead of cloud solutions?
While cloud-based AI offers certain benefits, it is not always the most suitable option for every scenario. Executing AI locally addresses several practical concerns that become increasingly significant as AI transitions from experimental phases to regular applications.
Privacy is a primary concern. Cloud models generally log prompts and outputs, frequently retaining this information for analysis or training purposes. For users handling sensitive files, personal data, or proprietary projects, utilizing AI directly on their PCs provides a sense of security.
Context is another drawback of cloud AI. Models without access to a user’s local files, datasets, or project structures may yield generic or inaccurate responses. On the other hand, local models can interact directly with directories, codebases, and documents, producing more precise and relevant results.
Cost also plays a critical role as AI usage increases. Many creative and development workflows depend on continual iteration—be it regenerating images, fine-tuning prompts, executing multiple inference passes, or testing various model options. Cloud service fees can escalate quickly in these situations, while running AI locally allows users to iterate freely without incurring individual request costs or hitting usage limits.
Control and security are becoming increasingly vital as AI agents enhance their capabilities. New AI tools can execute actions within a user’s system, such as modifying files, executing scripts, or automating workflows. Many users prefer maintaining this level of autonomy locally to retain full control.
The caveat is that modern AI models demand considerable computational resources, efficient memory usage, and hardware capable of adapting to the rapidly evolving software landscape.
What distinguishes RTX?
At the core of RTX GPUs are dedicated Tensor Cores, engineered specifically to accelerate AI tasks. Unlike CPUs or typical graphics hardware, Tensor Cores are crafted to optimize the matrix operations foundational to contemporary AI.
In practical terms, this results in significantly faster performance for activities like image generation, video enhancement, and large language model (LLM) inference. Workloads that may take several minutes or be impractical on CPU-only systems can run effectively on RTX GPUs.
This advantage is especially pronounced in visual AI. For instance, generating a video clip on an RTX GPU can take merely a few minutes, whereas comparable tasks on non-accelerated platforms might take five to ten times longer, depending on the workload and configuration. RTX GPUs also accommodate advanced precision formats such as FP4, which help decrease memory requirements while boosting throughput for AI inference.
The AI software ecosystem advantage
Hardware performance is futile without compatible software. AI evolves rapidly, making access to the newest tools and frameworks essential.
The same CUDA ecosystem that supports
Other articles
 The Samsung Galaxy S26 could provide an incredibly rapid AI image feature that operates without an internet connection.
There are rumors that the Galaxy S26 will include EdgeFusion, an offline text-to-image tool designed for quick results in under a second. If this feature is genuine, factors such as battery life, heat generation, and integration will determine its usability.
The Samsung Galaxy S26 could provide an incredibly rapid AI image feature that operates without an internet connection.
There are rumors that the Galaxy S26 will include EdgeFusion, an offline text-to-image tool designed for quick results in under a second. If this feature is genuine, factors such as battery life, heat generation, and integration will determine its usability.
 Support for the Galaxy S21 is coming to an end, which impacts the security updates you will receive.
Samsung’s Galaxy S21 security updates have become more unpredictable. The S21 series is no longer included in Samsung's monthly and quarterly update lists, which is significant for those who depend on banking, work logins, and other sensitive applications.
Support for the Galaxy S21 is coming to an end, which impacts the security updates you will receive.
Samsung’s Galaxy S21 security updates have become more unpredictable. The S21 series is no longer included in Samsung's monthly and quarterly update lists, which is significant for those who depend on banking, work logins, and other sensitive applications.
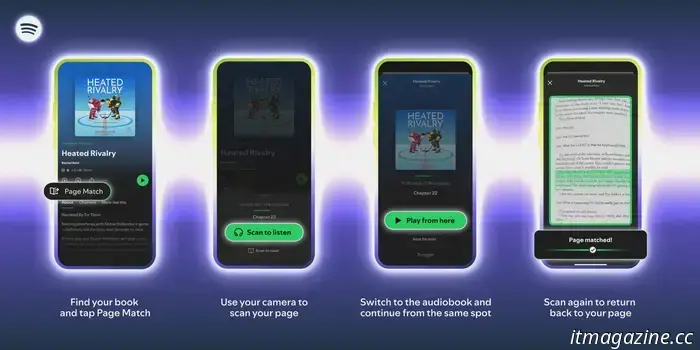 Spotify's latest Page Match feature can synchronize your audiobooks with print books.
With Page Match, Spotify addresses a common issue for readers, allowing you to flick through a page and quickly access the corresponding moment in the audiobook, facilitating a seamless combination of reading and listening during the day.
Spotify's latest Page Match feature can synchronize your audiobooks with print books.
With Page Match, Spotify addresses a common issue for readers, allowing you to flick through a page and quickly access the corresponding moment in the audiobook, facilitating a seamless combination of reading and listening during the day.
 Spotify is set to allow users to purchase physical books directly through the app.
Spotify is broadening its horizons by collaborating with Bookshop to offer physical books, enabling users to purchase paperbacks and hardcovers linked to titles they find in the app.
Spotify is set to allow users to purchase physical books directly through the app.
Spotify is broadening its horizons by collaborating with Bookshop to offer physical books, enabling users to purchase paperbacks and hardcovers linked to titles they find in the app.
 This app encourages you to engage with interactive media rather than watch viral videos.
Gizmo is a new application that substitutes viral videos with a TikTok-like feed featuring interactive, user-created mini apps for users to interact with.
This app encourages you to engage with interactive media rather than watch viral videos.
Gizmo is a new application that substitutes viral videos with a TikTok-like feed featuring interactive, user-created mini apps for users to interact with.
 Amazon is utilizing AI to reduce expenses in film and TV production.
Amazon is putting money into new AI technologies to simplify film and TV production while reducing expenses.
Amazon is utilizing AI to reduce expenses in film and TV production.
Amazon is putting money into new AI technologies to simplify film and TV production while reducing expenses.
Why NVIDIA RTX PCs provide the optimal solution for running AI locally.
NVIDIA's RTX AI PCs bring data center-level AI capabilities to desktop environments, enabling creators and developers to execute sophisticated models locally, with increased speed and enhanced control.
